1. Introduction
1.1. What is spam?
To spam is to mass-mail unrequested identical or nearly-identical email messages, particularly those containing advertising. Especially used when the mail addresses have been culled from network traffic or databases without the consent of the recipients (see the Linux Dictionary).
Firewalls do not protect you against spam, but you can use other software to identify and filter out junk email.
1.3. Email software components
1.3.1. Incoming mail
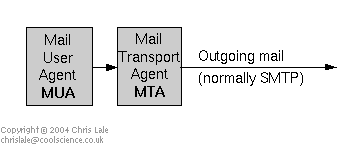
The type of software that manages email on your computer falls into three loosely defined catagories: Mail Transport Agent, Mail Delivery Agent and Mail User Agent. There is an article describing generic mail flow. These mail agents are often incorporated into a single software application (eg evolution, mozilla mail, etc). Figure 1 shows a typical system for receiving email.
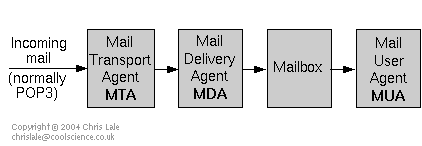
Figure 1: the major components of a mail system dealing with incoming mail.
Mail Transport Agent (MTA), sometimes referred to as a Mail Transfer Agent. A mail transport agent is software that enables mail to travel from one mail system to another. Your provider's server uses an MTA to send you your mail. You must have an MTA at your end of the connection. A standard Debian installation uses exim, but you may come across others eg sendmail, smail, qmail, etc. Typically, the MTA passes the mail onto an MDA.
Mail Delivery Agent (MDA), sometimes referred to as a Local Delivery Agent (LDA). A mail delivery agent is software that takes mail from an MTA and passes it on to a mailbox or another MTA. A standard Debian installation uses procmail, although there are others eg deliver.
Mail User Agent (MUA). A mail user agent is the software that enables a user to write, send, receive and read email. A standard Debian installation uses mail for local mail. Other mail user agents include elm, pine, eudora, pegasus, etc.
Mail from your provider normally reaches you using the POP3 protocol. A protocol is a set of rules that govern how things communicate over the network (see theLinux dictionary).
1.4. Mail on a Debian system
1.4.1. Debian local mail
A user can read the mail using mail as the MUA. The command is:
mail
|
mail local-user-2
|
1.4.4. Example of a spam email modified using spamassassin
1.4.4.1. Added headers
X-Spam-Status: Yes, hits=5.7 required=5.0
tests=VIAGRA,BASE64_ENC_TEXT,SUBJ_ALL_CAPS version=2.20
X-Spam-Flag: YES
X-Spam-Level: *****
X-Spam-Checker-Version: SpamAssassin 2.20
(devel $Id: x27.html.en,v 1.1 2004/04/30 21:50:38 chrislale Exp $)
X-Spam-Prev-Content-Type: text/plain
X-Spam-Prev-Content-Transfer-Encoding: base64
X-Evolution-Source: mbox:/var/mail/local-user
|
1.4.4.2. Modified subject line
spamassassin also modifies the subject line of suspected spam.
Subject: *****SPAM***** WEEKEND VIAGRA
|
1.4.4.3. Lines added to the top of the message
SPAM: -------------------- Start SpamAssassin results ----------------------
SPAM: This mail is probably spam. The original message has been altered
SPAM: so you can recognise or block similar unwanted mail in future.
SPAM: See http://spamassassin.org/tag/ for more details.
SPAM:
SPAM: Content analysis details: (5.7 hits, 5 required)
SPAM: Hit! (2.4 points) BODY: Plugs Viagra
SPAM: Hit! (1.4 points) Message text disguised using base-64 encoding
SPAM: Hit! (1.9 points) Subject is all capitals
SPAM:
SPAM: -------------------- End of SpamAssassin results ---------------------
|
1.6. Information you need before you start
Information you need | Details of the account with your provider |
your provider's telephone number |
|
the address of your provider's POP3 server (for your incoming mail) |
|
your username for logging in to the POP3 server |
|
your password for logging in to the POP3 server |
|
the address of your provider's SMTP server (for your outgoing mail) |
|
1.7. Names used in this document
1.7.1. Names used on your (local) computer
Pseudonym | Description | Real name on your system |
firstname surname | your full name |
|
local-host | the name of your (local) computer. (You can find out by entering hostname at the command prompt |
|
local-user or local-user@local-host | your username on the local computer |
|
Example | the account name used evolution to identify your provider (eg the provider's name) |
|
1.7.2. Names used on your provider's (remote) server
Pseudonym | Description | Real name on your system |
remote-user-name | your username on the remote server (isp or hosted server) |
|
remote-user-name@example.net | the name of your account on the remote server |
|
mail.example.net | the name of the remote POP3 mail server (that your incoming mail comes from) |
|
smtp.example.net | the name of the remote SMTP mail server (that your outgoing mail goes to) |
|